Übersichtliches Zeichnen von Graphen
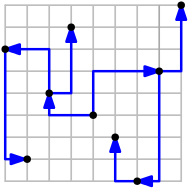
Graphen sind nicht nur ein häufiges Hilfsmittel beim Modellieren und Lösen von Problemen in der Informatik, sondern werden auch oft zur Visualisierung von Daten genutzt. Auch für Laien sind konkrete Zeichnungen von Graphen oft gut verständlich, da die Darstellung einer Verbindung oder eines Zusammenhangs durch Kanten intuitiv ist. Darüber hinaus lassen sich Methoden zum Zeichnen von Graphen auch oft für das Zeichnen realer Netzwerke, wie z.B. (U-)Bahnnetze, verwenden. Wir entwickeln und untersuchen Algorithmen für das übersichtliche Zeichnen von Graphen.
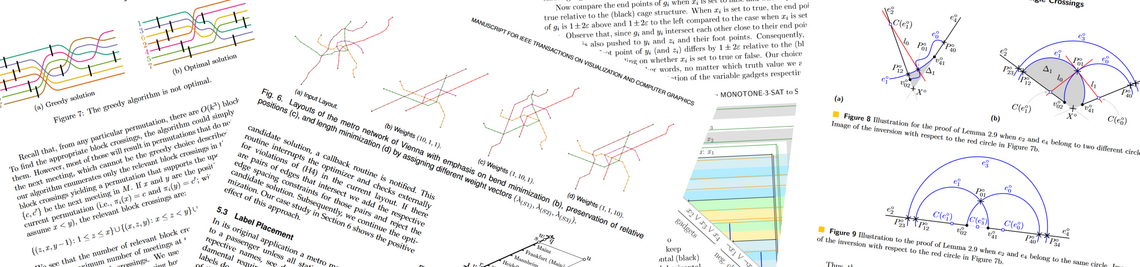
Es gibt auf dem Gebiet des Graphenzeichnens zwar schon viele beweisbar gute Algorithmen, die aber dennoch keine wirklich übersichtlichen Zeichnungen produzieren. Dies liegt daran, dass es meist schon schwer ist, nur ein gewünschtes Zielkriterium zu optimieren, wie z.B. die Anzahl der Knicke oder der Kreuzungen von Kanten. Dies führt dazu, dass andere Anforderungen an die Übersichtlichkeit einer Zeichnung nicht erfüllt werden, etwa weil die Kanten sehr lang sind oder einzelne Kanten sehr viele Knicke aufweisen. Es kann daher auch sinnvoll sein, Teilprobleme nicht optimal zu lösen, sondern gegeneinander abzuwägen. So kann eine Zeichnung besser lesbar werden, wenn es ein paar Kantenkreuzungen mehr gibt, dafür aber die Kreuzungswinkel sehr groß sind, wodurch die einzelne Kreuzung sehr viel übersichtlicher wird.
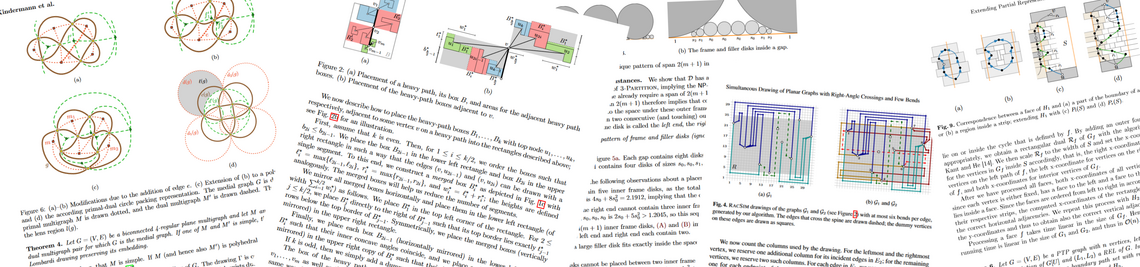
Die meisten existierenden Zeichenalgorithmen funktionieren außerdem nur auf planaren Graphen, d.h. Graphen, die sich ohne Überschneidungen zeichnen lassen. Gerade auf realen Daten basierende Graphen sind allerdings oft nicht planar. Haben solche Graphen eine gewisse Größe, was nicht ungewöhnlich ist, so sind in einer Zeichnung die einzelnen Knoten und Kanten ohnehin kaum unterscheidbar. Um die Graphen dennoch vernünftig darstellen zu können, existieren verschiedene Ansätze: man bündelt Gruppen von Kanten oder bildet Knotencluster. Es existiert jedoch noch kein Verfahren, das stets übersichtliche Zeichnungen liefert.
Projektmitarbeiter
- Alexander Wolff
- Boris Klemz
- Oksana Firman
- Johannes Zink
- Felix Klesen
- Tim Hegemann
- Marie Diana Sieper
- Jonathan Klawitter (bis 2021)
- Myroslav Kryven (bis 2021)
- André Löffler (bis 2020)
- Steven Chaplick (bis 2020)
- Philipp Kindermann (bis 2020)
- Fabian Lipp (bis 2018)
- Martin Fink (bis 2014)
Veröffentlichungen
-
Stick Graphs with Length Constraints. . In Proc. 27th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 11904 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, D. Archambault, C. D. Tóth (Hrsg.), S. 3–17. Springer-Verlag, 2019.
-
Computing Optimal-Height Tangles Faster. . In Proc. 27th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 11904 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, D. Archambault, C. D. Tóth (Hrsg.), S. 203–215. Springer-Verlag, 2019.
-
Compact Drawings of 1-Planar Graphs with Right-Angle Crossings and Few Bends. . In Computational Geometry: Theory and Applications, 84, S. 50–68. 2019.
-
Drawing Graphs on Few Circles and Few Spheres. . In Journal of Graph Algorithms & Applications, 23(2), S. 371–391. 2019.
-
Orthogonal and Smooth Orthogonal Layouts of 1-Planar Graphs with Low Edge Complexity. . In Proc. 26th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 11282 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, T. Biedl, A. Kerren (Hrsg.), S. 509–523. Springer-Verlag, 2018.
-
On the Maximum Crossing Number. . In Journal of Graph Algorithms & Applications, 22(1), S. 67–87. 2018.
-
Beyond Outerplanarity. . In Proc. 25th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 10692 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, F. Frati, K.-L. Ma (Hrsg.), S. 546–559. Springer-Verlag, 2018.
-
Compact Drawings of 1-Planar Graphs with Right-Angle Crossings and Few Bends. . In Proc. 26th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 11282 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, T. Biedl, A. Kerren (Hrsg.), S. 137–151. Springer-Verlag, 2018.
-
Planar {L}-Drawings of Directed Graphs. . In Proc. 25th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 10692 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, F. Frati, K.-L. Ma (Hrsg.), S. 465–478. Springer-Verlag, 2018.
-
Computing Storylines with Few Block Crossings. . In Proc. 25th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 10692 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, F. Frati, K.-L. Ma (Hrsg.), S. 365–378. Springer-Verlag, 2018.
-
Snapping Graph Drawings to the Grid Optimally. . In Proc. 24th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 9801 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Y. Hu, M. Nöllenburg (Hrsg.), S. 144–151. Springer-Verlag, 2016.
-
Obstructing Visibilities with One Obstacle. . In Proc. 24th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 9801 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Y. Hu, M. Nöllenburg (Hrsg.), S. 295–308. Springer-Verlag, 2016.
-
Block Crossings in Storyline Visualizations. . In Proc. 24th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 9801 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Y. Hu, M. Nöllenburg (Hrsg.), S. 382–398. Springer-Verlag, 2016.
-
Faster Force-Directed Graph Drawing with the Well-Separated Pair Decomposition. . In Proc. 23rd Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 9411 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, E. {Di Giacomo}, A. Lubiw (Hrsg.), S. 52–59. Springer-Verlag, 2015.
-
Pixel and Voxel Representations of Graphs. . In Proc. 23rd Int. Symp. Graph Drawing & Network Vis. (GD), Bd. 9411 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, E. {Di Giacomo}, A. Lubiw (Hrsg.), S. 472–486. Springer-Verlag, 2015.
-
Luatodonotes: Boundary Labeling for Annotations in Texts. . In Proc. 22nd Int. Sympos. Graph Drawing (GD), Bd. 8871 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, C. Duncan, A. Symvonis (Hrsg.), S. 76–88. Springer-Verlag, 2014.
-
On Monotone Drawings of Trees. . In Proc. 22nd Int. Sympos. Graph Drawing (GD), Bd. 8871 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, C. Duncan, A. Symvonis (Hrsg.), S. 488–500. Springer-Verlag, 2014.
-
Drawing Graphs within Restricted Area. . In Proc. 22nd Int. Sympos. Graph Drawing (GD), Bd. 8871 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, C. Duncan, A. Symvonis (Hrsg.), S. 367–379. Springer-Verlag, 2014.
-
Drawing Graphs with Vertices at Specified Positions and Crossings at Large Angles. . In Proc. Workshop Algorithms Comput. (WALCOM), Bd. 7157 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, {Md. S. Rahman, {Shin- ichi} Nakano (Hrsg.), S. 186–197. Springer-Verlag, 2012.
-
Drawing (Complete) Binary Tanglegrams: Hardness, Approximation, Fixed-Parameter Tractability. . In Algorithmica, 62(1--2), S. 309–332. 2012.
-
Schematization in Cartography, Visualization, and Computational Geometry. . In Bd. 10461 von Dagstuhl Seminar Proceedings. Schloss Dagstuhl – Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik, 2011.
-
Drawing and Labeling High-Quality Metro Maps by Mixed-Integer Programming. . In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 17(5), S. 626–641. 2011.
-
Manhattan-Geodesic Embedding of Planar Graphs. . In Proc. 17th Int. Sympos. Graph Drawing (GD), Bd. 5849 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, D. Eppstein, E. R. Gansner (Hrsg.), S. 207–218. Springer-Verlag, 2010.
-
Untangling a Planar Graph. . In Discrete & Computational Geometry, 42(4), S. 542–569. 2009.
-
Drawing Binary Tanglegrams: An Experimental Evaluation. . In Proc. 11th Workshop Algorithm Engineering and Experiments (ALENEX), S. 106–119. 2009.
-
Cover Contact Graphs. . In Proc. 15th Int. Sympos. Graph Drawing (GD), Bd. 4875 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, S.-H. Hong, T. Nishizeki, W. Quan (Hrsg.), S. 171–182. Springer-Verlag, 2008.
-
Straightening Drawings of Clustered Hierarchical Graphs. . In Proc. 33rd Int. Conf. Current Trends Theory & Practice Comput. Sci. (SOFSEM), Bd. 4362 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, J. van Leeuwen, G. F. Italiano, W. van der Hoek, C. Meinel, H. Sack, F. Plášil (Hrsg.), S. 177–186. Springer-Verlag, 2007.
-
Boundary Labeling: Models and Efficient Algorithms for Rectangular Maps. . In Computational Geometry: Theory and Applications, 36(3), S. 215–236. 2007.
-
Drawing Subway Maps: A Survey. . In Informatik – Forschung & Entwicklung, 22(1), S. 23–44. 2007.
-
Minimizing Intra-Edge Crossings in Wiring Diagrams and Public Transport Maps. . In Proc. 14th Int. Sympos. Graph Drawing (GD), Bd. 4372 von Lecture Notes in Computer Science, M. Kaufmann, D. Wagner (Hrsg.), S. 270–281. Springer-Verlag, 2007.
-
{Geometrische Netzwerke und ihre Visualisierung}. . 2005, Juni.